Learn More
The hidden costs of buying a house

There are a number of extra, often seemingly hidden costs buyers need to be aware of, which aren’t necessarily spelled out in glossy real estate advertisements.
Upfront and hidden costs can add as much as $40,000 to the purchase price of a property, so it’s vital buyers understand them. Almost all of the costs depend on the value of the property being purchased and where it’s located.
Different state and territory governments, in charge of costs such as stamp duty and transfer fees, among others, and local councils, who are responsible for calculating rates, also charge different amounts, as do banks and lenders.
In some states, first-home buyers don’t have to pay one of the biggest “add-ons”, stamp duty, but in others, they do. All this means it can be tricky to work out exactly how much will have to be paid.
Let’s take an example of a $500,000 property in Queensland. What are the upfront and hidden costs?
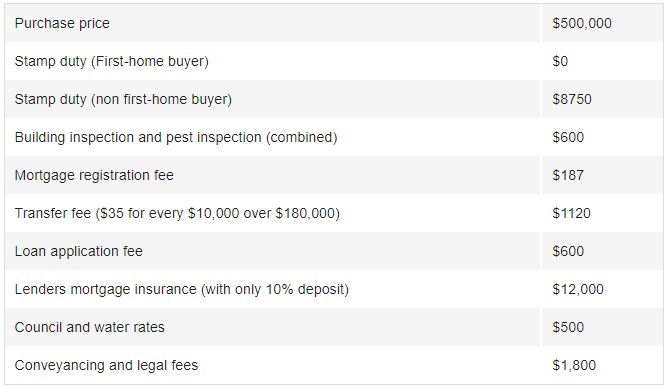
Hidden and total costs for buying a home

1. Conveyancing & legal fees
Conveyancing and legal fees are the costs associated with engaging a conveyancer or other professional to do the required legal paperwork when buying a home.
Dr Diaswati Mardiasmo, the chief economist for PRD, said conveyancing involves the preparation, execution, and lodgment of various legal documents to enable a swift and legal sale.
Typically there are three phases; preparation of sale contract, the exchange of contracts, and completion.
“Because conveyancing and legal fees can be somewhat standardised – because there is a similar process in the handling of each house sale – there is usually the option of selecting a fixed fee.
“However, it’s important to understand what is included in fixed fee conveyancing and ensure you don’t get caught out. For example, if there needs to be an extra letter sent from you, the buyer, to the owner, there might be an extra charge,” she said.
Dr Mardiasmo said conveyancing and legal fees depend on how complicated the transaction is and who does the work, ie a conveyancing company with a team of solicitors specialising in conveyancing or a private lawyer or solicitor.
Estimated cost
On average, conveyancing and legal fees come in at about $1,800. It is possible to “DIY it”, but it’s not recommended, given the complexity of the work.
2. Stamp duty
Stamp duty is a charge applied by state and territory governments and relates to the transfer of land or property.
Stamp duty can cost tens of thousands of dollars. The exact amount depends on the value of the property, the state or territory the property is in, if the purchaser is a first-home buyer, if it’s an established home, new home, or vacant land, and other factors.
The more expensive the home, the more stamp duty is. For example, a $1 million purchase can attract stamp duty as high as $55,000.
Several states offer stamp duty exemptions and concessions to first-home buyers. On a $500,000 house, first home buyers won’t pay any stamp duty in Victoria, New South Wales, or Queensland.
- New South Wales
- Queensland
- South Australia
- Tasmania
- Victoria
- Western Australia
- ACT
- Northern Territory
- New South Wales
- Queensland
- South Australia
- Tasmania
- Victoria
- Western Australia
- ACT
- Northern Territory
Estimated cost
- While in some states first-home buyers don’t have to buy any stamp duty, in others, for a $500,00 house, it can range from $21,330 (South Australia) to $13,433 (Western Australia) for first-home buyers and $17,707 (New South Wales) to $21,970 (Victoria) for others.
3. Pest & building inspections
A building inspection is an assessment of a property’s condition done by a qualified inspector, usually before putting in an offer on a property, although an offer can be made conditional on one.
It covers everything from faulty roofs to rising damp and cracked walls, and generally includes information on whether these faults can be repaired and how much repairs would cost.
A lot of buyers ask their inspectors to check for pest damage during the inspection, too. This usually costs a little extra, but is generally advisable, given the extensive damage termites and other pests can cause.
“There are rare cases in which a pest and building inspection is waived; usually this is only for off-the-plan, newly built properties and only if the developer/builder provides certificates to show that they have done their checks, to ensure the property is up to government standard and signed contract with you,” Dr Mardiasmo said.
Estimated cost
- The cost of a pest and building inspection varies from state to state, and inspectors operating in metropolitan areas generally charge more than those working in regional areas. However, they usually come in at $600.
4. Mortgage registration & transfer fees
- Mortgage registration and transfers fees are the costs associated with formally registering a mortgage and transferring the property ownership. The costs for each differ between states. Some charge a set fee, while others are on a sliding scale.
Mortgage registration fee
Dr Mardiasmo said a mortgage registration fee is paid when a mortgage is established or discharged – paid out – against a property.
“The land titles office in each state or territory collects the fee for registering the lenders’ mortgage on the title record for the property.”
Transfer fee
The transfer fee is set by the relevant state government and covers the transfer of title of the property from one party to another.
Estimated costs
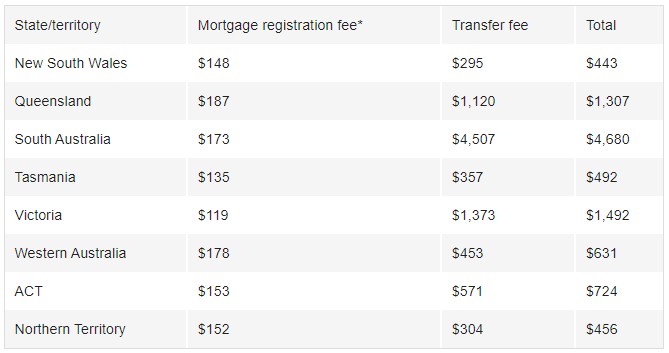
Based on a $500,000 purchase price
* $35 for every $10,000 over $180,000
5. Loan application or establishment fees
Loan application or establishment fees are the costs associated with setting up a loan with a lender.
According to Dr Mardiasmo, the fees payable depend on the lender, the loan amount, and other factors. They can be a fixed fee or a percentage of the loan amount. “This may also differ if you’re using a mortgage broker,” she said.
Some lenders will waive these types of fees under certain circumstances.
Estimated cost
The application or establishment fees are generally about $600, though they can be more than $1000, depending on the loan and lender.
6. Lenders’ Mortgage Insurance (LMI)
Lenders’ mortgage insurance (LMI) is a fee banks and other lenders charge borrowers when they’re deemed high risk. Usually, this is when the deposit is less than 20% of their property’s purchase price or those applying have inconsistent income.
Technically, the borrower pays the LMI payment in a lump sum at settlement. However, many lenders will offer to finance LMI into the home loan, so it’s added to the monthly mortgage payments. This means borrowers don’t have to have the funds upfront, but it also means paying more interest on the overall loan, resulting in higher monthly repayments.
Estimated cost
Each LMI provider calculates the cost slightly differently, but the amount payable depends on the size of the loan, the deposit, the applicants’ employment status, and other factors. Dr Mardiasmo said on a $500,000 property, with only a 10% deposit, the LMI would be about $12,000.
7. Council and water rates
Council and water rates are another two expenses buyers have to consider when buying property.
Council rates
The seller will have paid any rates owing to the local council – generally until the end of the quarter – and they simply add the buyer’s portion of that amount to the purchase price.
Dr Mardiasmo said council rates are determined by the local council, usually depending on a land valuation. “Land valuations are usually performed annually by the state government,” she said.
Water rates
While most utilities, like power and gas, will be cut off and then reconnected as part of a sale, with water charges, there is crossover.
The seller is generally required to pay for all the water used up to the settlement date. A special water meter reading is usually done to confirm the amount and then the buyer takes over.
Estimated cost
As each local council and water authority charge differently, the cost of council and water rates varies across the country. It can cost anything from $500 in Queensland to $4134 in Western Australia.
8. Insurance
Insurance – both home and contents – are other immediate and ongoing costs after buying a home.
Home insurance, sometimes called property or building insurance, generally covers a main dwelling, a garage, other outbuildings that can be locked, and items “permanently attached or fixed” to a home such as light fixtures and built-in wardrobes.
Contents insurance, on the other hand, covers things inside a home that aren’t permanently fixed to the walls or floor, like furniture, TVs, and fridges.
Both protect against a wide range of events such as fire, storm, and flood damage.
A home and contents policy combines the two types of cover. It’s possible to have one policy for the home and another for contents, but most people combine them into one.
The cost of any insurance policy is based on the “sum insured” and the risk of needing to make a claim.
Insurers look at several factors when calculating a premium, including the number of people living in the home, the age of the person getting the insurance, the location of the property, and the crime rate of the suburb.
Estimated cost
Given the number of variables taken into account when calculating premiums, the cost for insurance varies greatly across the country.
Comparison website finder.com.au analysis shows the average home and contents policy – to cover a house worth $500,000 and contents valued at $100,000 – is $136.73 a month.
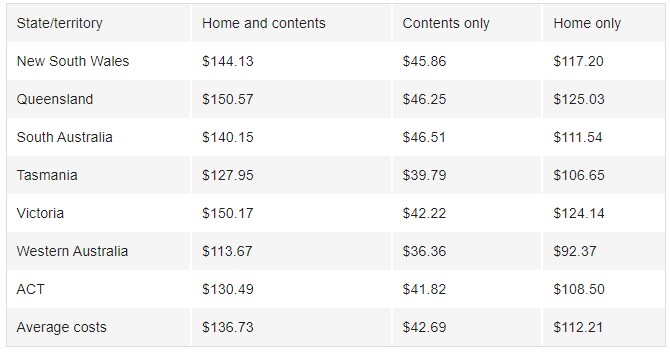
*February 2021
10. Moving
An extra cost some forget about when buying a property is the cost of actually moving in there.
The cost of moving depends on many and varied factors, including where the move is from and to, how much needs to be moved and so.
Many removalists charge by the hour, while interstate removalists tend to charge by cubic metres or by the number of boxes
Quotes are likely to range from $75 to $300 an hour – and may or may not include insurance or packing materials – so it’s wise to clarify when getting a quote.
For about $250 an hour, it’s possible to include premium insurance to cover damage caused during packing and unpacking.
Many removalists have calculators on their websites, to help clients add up the cost of a move. The final fee will depend on how many rooms are included and whether heavy or awkward items are included.
According to Hipages.com.au, an online platform that connects Australians with tradies, the following costs are common.
- $110/hr for moving small items, using two movers, and taking two to three hours
- $125/hr for a one-bedroom apartment, using two movers and taking three to five hours
- $175/hr for a small three-bedroom apartment, using three movers and taking four to six hours
- $245/hr for a large three-bedroom home, using four movers and taking six to eight hours
- $315/hr for a large family home, 4-bedrooms-plus using five movers and taking seven to nine hours.
Estimated cost
On average, the cost of moving falls somewhere between $300 and $3,500. An interstate move can be much more. To pack and move a standard “house load” from Melbourne to Brisbane, it’s between $6,500 and $6,500, plus insurance.
11. Investment property costs
When buying a property as an investment rather than to live in, there are extra costs to take into consideration.
These can include:
- leasing fees
- property management fees
- repairs and maintenance to ensure minimum rental standards
- body corporate fees
- tax
- loan, interest, and bank fees.
Estimated cost
The costs involved in running an investment property are hugely variable and depend on many factors.
The information in this article is for general interest and is not intended as advice. For advice and planning, consult an experienced financial planner.
*Upfront and hidden costs of buying a house was written by Erin Delahunty and published on Realestate.com.au